Urological conditions affect the urinary system and reproductive organs, and they can vary widely in terms of severity and impact. Both men and women can experience a range of urological issues, from mild discomfort to more serious, chronic conditions. In this post, we’ll explore some of the most common urological conditions, their symptoms, and the importance of seeking medical advice when needed.
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when bacteria enter the urinary system, causing inflammation and infection. UTIs are among the most common urological conditions, especially in women, though men can also be affected.
Symptoms:
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain
If left untreated, UTIs can lead to kidney infections or other serious complications. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of the above symptoms.
2. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a condition in which the prostate gland enlarges, often affecting men as they age. This condition is non-cancerous but can cause significant symptoms related to urination.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
- Feeling that the bladder isn’t fully emptied
- Urgency to urinate
Although BPH is not cancerous, the symptoms can be bothersome and may require treatment to relieve discomfort and improve urinary flow.
3. Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile dysfunction (ED) refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. It’s a common condition, especially in older men, but can affect men of any age.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection
- Reduced sexual desire or satisfaction
- Anxiety or stress related to sexual performance
ED can be caused by various factors, including underlying health conditions (diabetes, hypertension), stress, or hormonal imbalances. It is important to discuss symptoms with a doctor to determine the cause and explore treatment options.
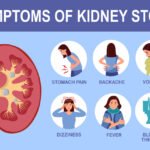
4. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause intense pain when they pass through the urinary tract. This condition can affect both men and women, though it is more common in men.
Symptoms:
- Severe pain in the lower back, side, or abdomen
- Painful urination
- Blood in the urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Frequent urge to urinate
Kidney stones can range in size, and smaller stones may pass without much discomfort, but larger stones can cause significant pain and may require medical treatment to remove them.
5. Bladder Incontinence
Bladder incontinence refers to the inability to control urination, leading to accidental leaks of urine. This condition is more common in older adults and can affect both men and women. It may be caused by weakened bladder muscles, nerve damage, or other health conditions.
Symptoms:
- Frequent need to urinate with little warning
- Leaking urine during physical activity, laughing, or coughing
- Inability to control urination
- Sudden, intense urge to urinate
There are different types of incontinence, including stress incontinence, urge incontinence, and overflow incontinence. Treatment options range from lifestyle changes to medications and, in some cases, surgery.
6. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men, typically affecting older men. In the early stages, prostate cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms, but as the cancer grows, symptoms may arise.
Symptoms:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Painful ejaculation or discomfort in the pelvic area
Prostate cancer can be treated effectively if caught early, which is why regular screenings (like a prostate-specific antigen, or PSA, test) are crucial for men over the age of 50, or those at higher risk.
7. Overactive Bladder (OAB)
An overactive bladder (OAB) is a condition that causes a sudden and uncontrollable urge to urinate, often leading to frequent bathroom trips. It can be related to bladder dysfunction or nerve issues.
Symptoms:
- Urgent need to urinate, even with little urine in the bladder
- Frequent urination during the day and night
- Accidental leakage of urine due to the sudden urge
- Difficulty holding urine until reaching the restroom
OAB can significantly affect a person’s quality of life. Treatment often includes medications, lifestyle changes, or bladder training exercises.
8. Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer is a relatively rare but serious condition that affects men, typically between the ages of 15 and 35. The symptoms of testicular cancer often involve a painless lump or swelling in one of the testicles.
Symptoms:
- A painless lump or swelling in one or both testicles
- Discomfort or a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- Pain in the lower abdomen or groin
- Back pain (in advanced stages)
Testicular cancer is highly treatable, especially if detected early. Men are encouraged to perform regular self-examinations and seek medical attention if they notice any unusual changes.
9. Interstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome)
Interstitial cystitis (IC), also known as painful bladder syndrome, is a chronic condition that causes bladder pain and pressure, as well as frequent urination.
Symptoms:
- Chronic pelvic pain or pressure
- Increased frequency of urination (day and night)
- Painful urination, but without an infection
- Pain during sexual intercourse
While the exact cause of IC is unknown, it is often associated with inflammation in the bladder lining. Treatment may include medications, dietary changes, and physical therapy.
10. Urinary Tract Obstruction
Urinary tract obstruction occurs when there is a blockage in the urinary system, which can be caused by kidney stones, tumors, or an enlarged prostate. This condition can result in urine retention and may cause kidney damage if left untreated.
Symptoms:
- Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or back
- Difficulty urinating or an inability to urinate
- Blood in the urine
- Frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Depending on the cause of the obstruction, treatment may involve medications, surgery, or other interventions to remove the blockage and restore normal urinary function.
Conclusion
Urological conditions are diverse and can affect both men and women of all ages. Recognizing the symptoms early is essential to prevent complications and improve outcomes. If you experience any of the symptoms described in this post, it’s important to consult a urologist who can diagnose the issue and recommend appropriate treatment. Early intervention can lead to better management of symptoms and overall urological health.