Urological conditions can affect the urinary tract and reproductive organs, impacting overall health and quality of life. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for managing these conditions effectively. This guide explores the most common urological disorders and their treatment options.
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are bacterial infections that can affect the bladder, urethra, or kidneys. They are more common in women but can also occur in men and children. Symptoms include a burning sensation while urinating, frequent urge to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pain in the lower abdomen or back. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, drinking plenty of water, and preventive measures like cranberry supplements and proper hygiene.
2. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys. They can vary in size and may cause severe pain. Common symptoms are sharp pain in the back or side, blood in urine, nausea, and difficulty passing urine. Treatments include medications to manage pain, shock wave lithotripsy to break stones, and surgery for larger stones.
3. Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of bladder control, common among older adults but occurring at any age. Symptoms include leakage during activities like coughing or laughing and frequent or urgent needs to urinate. Treatments range from pelvic floor exercises and medications to surgical options for severe cases.
4. Prostate Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia – BPH)
BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that can cause urinary issues in men, especially as they age. Symptoms include difficulty starting urination, a weak urine stream, and frequent urination, especially at night. Treatment options include medications like alpha-blockers and minimally invasive procedures such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
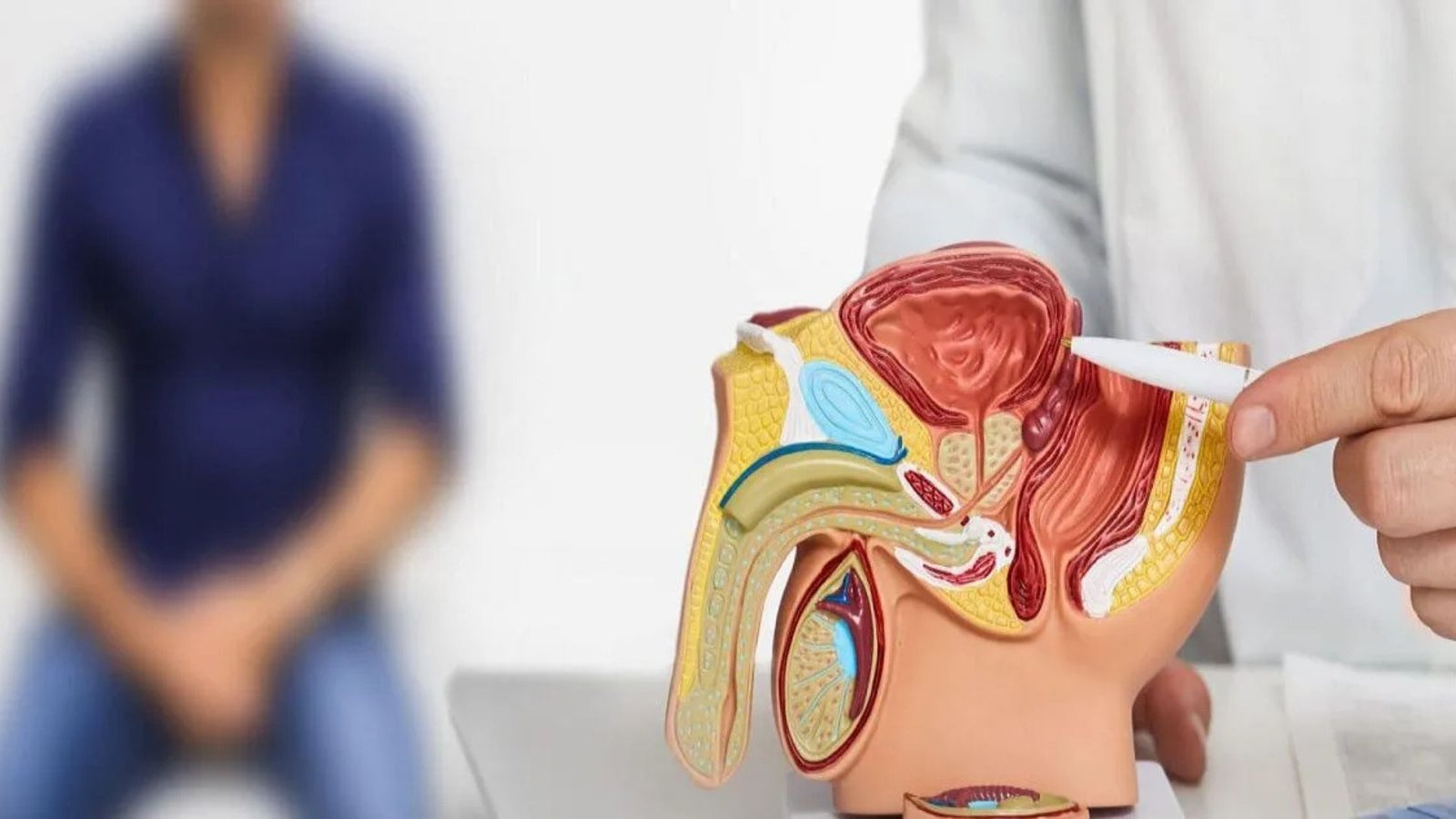

5. Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
ED is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection suitable for sexual activity. Symptoms include difficulty getting or keeping an erection and reduced sexual desire. Treatments involve medications such as phosphodiesterase inhibitors, lifestyle changes like regular exercise and a healthy diet, and counseling for psychological causes.
6. Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer typically begins in the lining of the bladder and can spread if untreated. Symptoms include blood in urine, frequent or painful urination, and back or pelvic pain. Treatment options include surgery to remove tumors, chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy to boost the immune system.
7. Overactive Bladder (OAB)
OAB causes a sudden and frequent urge to urinate, often disrupting daily life. Symptoms include a sudden urge to urinate, increased frequency of urination, and waking up at night to urinate. Treatments include behavioral therapy like bladder training, medications to relax bladder muscles, and Botox injections for severe cases.
Conclusion
Urological conditions are common but often manageable with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Whether dealing with kidney stones, UTIs, or prostate issues, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for effective management. Taking proactive steps like maintaining hydration, practicing good hygiene, and staying informed can further reduce risks and improve overall urological health.