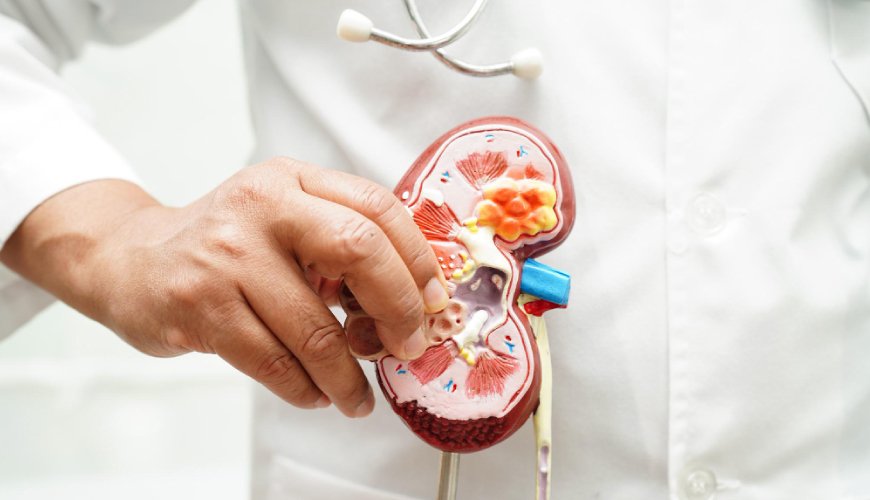
A urologist is a medical specialist who diagnoses and treats a wide range of conditions related to the urinary tract and the male reproductive system. Urologists are highly trained to handle issues affecting the kidneys, bladder, urethra, prostate, and testicles. If you’re experiencing urinary problems, discomfort, or reproductive health issues, a urologist can provide the care and expertise needed. This post will explore what urologists treat and when you should consider visiting one.
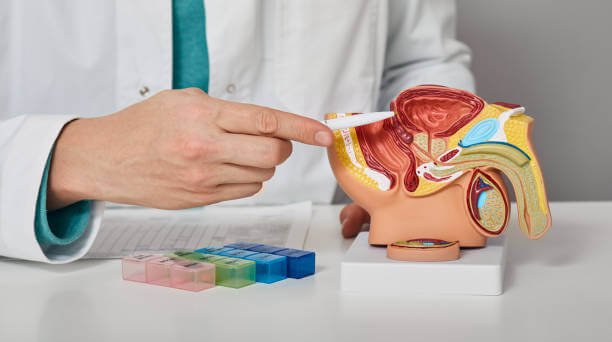
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common conditions treated by urologists, particularly in women. UTIs occur when bacteria invade the urinary system, causing inflammation and discomfort. Urologists can diagnose and treat infections that affect the bladder, urethra, or kidneys.
Symptoms:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
Treatment for UTIs often involves antibiotics to eliminate the infection. Urologists may also investigate the underlying cause of recurrent UTIs.
2. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain when they pass through the urinary tract. Urologists are skilled in diagnosing the size, location, and type of kidney stones, and they provide various treatment options, from medication to surgery.
Symptoms:
- Intense pain in the back, side, or abdomen
- Blood in the urine
- Frequent urination
- Nausea and vomiting
Small stones may pass on their own with plenty of fluids, but larger stones may require procedures such as shock wave lithotripsy (SWL), ureteroscopy, or surgery to remove them.
3. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) refers to the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, which can lead to urinary problems in men, especially as they age. Urologists treat BPH using medications or minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine stream
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Incomplete bladder emptying
For moderate to severe cases, treatments include medications, prostate surgery, or minimally invasive therapies such as laser surgery.
4. Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition where men are unable to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse. Urologists specialize in diagnosing the underlying causes of ED, which may include hormonal imbalances, poor blood flow, or psychological factors.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty getting or keeping an erection
- Reduced sexual desire
- Trouble achieving a firm erection during sexual activity
Treatment for ED can range from lifestyle changes (e.g., improving diet and exercise) to medications, therapy, or surgical interventions such as penile implants.
5. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a common cancer in men, typically affecting older individuals. Urologists play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating prostate cancer. They may perform diagnostic tests like a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, biopsies, and imaging studies to determine the presence and extent of cancer.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty urinating or a slow urine stream
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Painful ejaculation
- Persistent pain in the pelvic area or lower back
Treatment options for prostate cancer may include surgery (prostatectomy), radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and active surveillance for less aggressive cancers.
6. Bladder Problems
Urologists also treat various bladder conditions, such as bladder infections, bladder cancer, and overactive bladder (OAB). Bladder issues can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, urgency, and incontinence. A urologist can diagnose and treat these conditions to restore bladder function.
Symptoms of Bladder Issues:
- Frequent urination or urgency
- Painful urination
- Incontinence (leakage of urine)
- Blood in the urine
Treatment for bladder conditions may include medication, lifestyle changes, bladder training, or surgery, depending on the condition’s severity.
7. Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is the inability to control urination, leading to accidental leakage. Urologists treat different types of incontinence, including stress incontinence, urge incontinence, and overflow incontinence. The treatment plan may include lifestyle changes, physical therapy, medications, or surgery.
Symptoms:
- Leaking urine during physical activities like coughing, sneezing, or laughing (stress incontinence)
- Urgent need to urinate with accidents (urge incontinence)
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder, leading to leakage (overflow incontinence)
Urologists often recommend pelvic floor exercises, medications, or surgical interventions like sling surgery or bladder lifts.
8. Testicular Disorders
Urologists also diagnose and treat conditions affecting the testicles, such as testicular cancer, varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum), and epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis). Men experiencing any symptoms related to the testicles should seek a urologist’s care for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms:
- Lumps or swelling in the testicles
- Pain or tenderness in the testicles or scrotum
- Changes in the size or shape of the testicles
Early detection and treatment are key in managing testicular cancer, while conditions like varicocele can be treated with surgery or other interventions.
9. Male Infertility
Male infertility can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances, low sperm count, or physical blockages. Urologists specializing in male infertility assess the cause of infertility through tests like semen analysis and imaging studies, providing treatment options to improve fertility.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty conceiving a child after one year of unprotected sex
- Abnormalities in sperm count or quality
Urologists may recommend medications, surgery, or assisted reproductive technologies (e.g., IVF) to address infertility issues.
10. Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a congenital condition in which the opening of the urethra is located on the underside of the penis instead of the tip. This condition requires surgical correction by a urologist, typically in infancy or early childhood.
Symptoms:
- Urethral opening located on the underside of the penis
- Curvature of the penis during erection
Surgical correction is often necessary to reposition the urethral opening and improve urinary and sexual function.
Conclusion
Urologists are specialists who treat a wide range of conditions related to the urinary system and male reproductive health. From common issues like UTIs and kidney stones to more complex conditions like prostate cancer and male infertility, urologists play a vital role in diagnosing and providing treatment for these conditions. If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, or if you’re concerned about your urinary or reproductive health, consulting a urologist is a wise step in getting the right care.