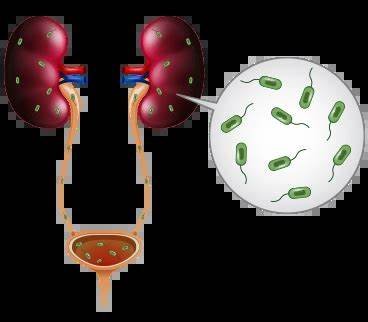
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common, but many people tend to overlook or dismiss the symptoms at first. While some cases can resolve on their own, it’s important to know when to seek medical help. Left untreated, a UTI can lead to severe complications, including kidney infections and sepsis. In this article, we’ll explore when you should see a doctor for a UTI and the signs that indicate professional intervention is necessary.
1. Early Symptoms of a UTI
The symptoms of a UTI typically begin in the lower urinary tract, affecting the bladder or urethra. These early signs should not be ignored, as they can worsen without treatment. Symptoms include:
- Painful urination: A burning or stinging sensation while urinating.
- Frequent urination: Feeling the urge to urinate often, even if little urine is passed.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine: Urine may appear cloudy or have a strong, unpleasant odor.
- Blood in urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, is a common sign of a UTI.
- Pelvic pain or pressure: Discomfort or pressure in the lower abdomen or pelvic area.
If you experience any of these symptoms, you should consider scheduling a visit with your doctor for diagnosis and treatment, especially if the symptoms persist for more than a day or worsen over time.
2. When to Seek Medical Help Immediately
In some situations, a UTI can escalate quickly and cause more severe health issues. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Severe pain: Intense pelvic or back pain, particularly if accompanied by fever, can indicate a kidney infection (pyelonephritis).
- Fever or chills: A fever, especially if it exceeds 100.4°F (38°C), can be a sign that the infection has spread to the kidneys or bloodstream.
- Nausea and vomiting: Feeling nauseous or vomiting, particularly with fever and back pain, can be signs of a serious kidney infection.
- Confusion or disorientation: This can be a sign of a systemic infection, especially in older adults, and may indicate sepsis.
These symptoms suggest that the infection may have spread beyond the bladder, requiring more urgent medical care to prevent serious complications.

3. When UTIs Occur in Vulnerable Populations
Certain groups of people are more vulnerable to UTIs and their complications. If you belong to one of these groups and experience symptoms of a UTI, it’s essential to consult with a doctor right away:
- Pregnant women: UTIs during pregnancy can pose risks for both the mother and the baby, including preterm labor or low birth weight. UTIs should be treated promptly to prevent complications.
- Older adults: UTIs in older adults can present with different or less noticeable symptoms, such as confusion or behavioral changes. If you or an elderly person experience these signs along with typical UTI symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
- People with diabetes: Diabetes can affect the immune system, making it harder to fight infections. If you have diabetes and experience UTI symptoms, see a doctor promptly to avoid complications.
- Individuals with urinary tract abnormalities: Those with structural issues like kidney stones or an enlarged prostate may be more prone to UTIs and should seek medical advice as soon as symptoms appear.
4. Recurrent UTIs and When to Seek Help
Some individuals experience recurrent UTIs, which can indicate an underlying issue that requires further investigation. If you have frequent UTIs (three or more in a year), it’s important to consult a doctor who may recommend additional tests or treatment options, such as:
- Urine culture: To identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic.
- Imaging tests: To check for structural abnormalities in the urinary tract that could be contributing to recurrent infections.
A healthcare provider may also discuss preventive strategies, such as low-dose antibiotics or lifestyle changes, to reduce the risk of future UTIs.
Advancements in Urology and Emerging Technologies
Urology conferences bring together experts from around the world to discuss the latest advancements in the field. These events highlight groundbreaking research, innovative treatments, and emerging technologies designed to improve patient care. As the medical industry embraces digital transformation, various sectors, including gaming and entertainment, continue to evolve rapidly. If you’re looking for a dynamic and engaging experience outside the medical field, wolfwinner casino offers a thrilling gaming platform with a vast selection of games.
5. Complications from Untreated UTIs
If left untreated, a UTI can lead to serious complications. The infection can ascend from the bladder to the kidneys, resulting in pyelonephritis, a kidney infection that can cause permanent kidney damage if not treated promptly. In some cases, UTIs can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening infection that spreads throughout the body. Signs of sepsis include rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, and confusion, and it requires immediate medical intervention.
6. When to See a Doctor for Children
UTIs in young children require medical attention, as they can lead to kidney damage or other complications if not properly treated. In infants and toddlers, symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Irritability or fussiness
- Poor feeding or drinking
If your child displays these symptoms or you suspect a UTI, consult a pediatrician to determine the best course of treatment.
7. The Importance of Timely Diagnosis and Treatment
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of a UTI are crucial to prevent complications. A doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection and may perform tests to rule out other underlying conditions. It’s essential to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
Conclusion
If you experience symptoms of a UTI, it’s important to seek medical attention to prevent the infection from worsening and leading to serious complications. Early treatment with antibiotics can often resolve the infection before it spreads to the kidneys or bloodstream. If you have recurrent UTIs or fall into a high-risk group, consult with your doctor for further evaluation and preventive care. The sooner you address the issue, the better the chances of avoiding complications and ensuring long-term urinary health.