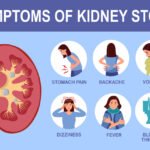
Kidney disease affects millions worldwide, often progressing silently until it reaches advanced stages. Urologists play a crucial role in preventing, diagnosing, and treating kidney-related conditions. Their expertise ensures optimal kidney health and helps mitigate the long-term effects of kidney disease.
Preventing Kidney Disease
1. Early Detection
Urologists focus on identifying risk factors and early signs of kidney disease. Regular check-ups and screenings can reveal:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes-related kidney issues
- Abnormal kidney function tests
2. Lifestyle Recommendations
Urologists often advise on lifestyle changes to support kidney health, such as:
- Maintaining a balanced diet low in sodium and processed foods
- Staying hydrated to prevent kidney stones
- Regular exercise to control blood pressure and weight
3. Managing Risk Factors
Urologists work with patients to manage conditions that may lead to kidney disease, including:
- Hypertension: Controlling blood pressure with medication and lifestyle changes
- Diabetes: Monitoring blood sugar levels and kidney function
Diagnosing Kidney Disease
1. Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Urologists use cutting-edge diagnostics to assess kidney health:
- Ultrasound: Detects kidney abnormalities, stones, or tumors
- Blood Tests: Measures creatinine and glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- Urinalysis: Identifies protein, blood, or other indicators of kidney dysfunction
2. Biopsy for Definitive Diagnosis
In cases of suspected kidney disease, urologists may perform a biopsy to determine the underlying cause and severity.
Treating Kidney Disease
1. Managing Kidney Stones
Urologists treat kidney stones with:
- Shockwave Lithotripsy (SWL): Non-invasive stone fragmentation
- Ureteroscopy: Removal of stones via a thin scope
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: Surgery for larger stones
2. Addressing Kidney Infections
Kidney infections (pyelonephritis) are treated with:
- Antibiotics to eliminate infection
- Monitoring for complications, such as abscess formation
3. Treating Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
For CKD, urologists collaborate with nephrologists to manage progression:
- Medications to control blood pressure and protein levels
- Dietary modifications to reduce kidney strain
- Monitoring for signs of kidney failure
4. Kidney Cancer Treatment
Urologists specialize in treating kidney cancers through:
- Surgery: Partial or total nephrectomy to remove tumors
- Ablative Therapies: Minimally invasive methods to destroy cancer cells
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system to fight cancer
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Urologists emphasize the need for routine kidney health assessments, especially for high-risk individuals. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes.
Conclusion
Urology plays a pivotal role in maintaining kidney health through prevention, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment. Partnering with a urologist ensures proactive management of kidney health, reducing the risk of severe complications and improving quality of life.