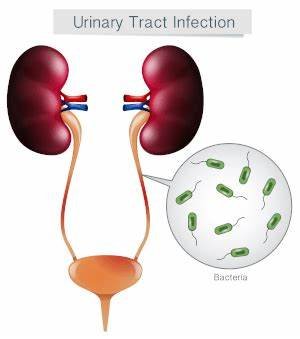
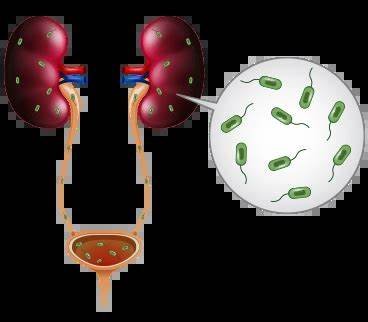
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue that can cause significant discomfort. One often overlooked factor in the development of UTIs is dehydration. Understanding how dehydration impacts urinary health and increases the risk of UTIs is essential for preventing these infections and maintaining overall urinary health.
How Dehydration Contributes to UTIs
Dehydration occurs when the body doesn’t get enough water to perform essential functions. When you’re dehydrated, your urine becomes more concentrated, meaning it has less water and more waste products. This concentrated urine can irritate the lining of the urinary tract, making it easier for bacteria to thrive and cause infections.
Additionally, dehydration leads to reduced urine production. Frequent urination is one of the body’s natural defenses against UTIs because it helps flush bacteria out of the urinary tract. When you’re dehydrated, you may urinate less frequently, allowing harmful bacteria to remain in the urinary system longer and increasing the chances of infection.
Why Proper Hydration Is Key in Preventing UTIs
Drinking adequate amounts of water helps dilute urine, making it less irritating to the urinary tract. It also ensures that your body produces enough urine to flush out bacteria before they can cause infections. By staying hydrated, you’re essentially providing your urinary system with the tools it needs to protect itself from harmful microorganisms.
Here are a few reasons why hydration is so important for preventing UTIs:
- Dilution of Urine: Well-hydrated urine is more dilute, which helps reduce irritation and prevents bacterial growth.
- Increased Urination: Proper hydration ensures frequent urination, which helps flush bacteria out of the urinary system.
- Support for Immune Function: Staying hydrated supports overall immune function, helping the body fight off infections more effectively.
How Much Water Should You Drink?
The amount of water needed for optimal hydration varies based on age, activity level, and overall health. A common recommendation is to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water a day, known as the “8×8 rule.” However, individual needs may vary, so it’s essential to listen to your body and drink when you’re thirsty. If you are physically active or in a hot climate, you may need more water to stay properly hydrated.
Signs of Dehydration to Watch Out For
Being aware of the signs of dehydration can help you take action before it negatively impacts your urinary health. Some common symptoms of dehydration include:
- Dry mouth and tongue
- Dark yellow or amber-colored urine
- Fatigue or dizziness
- Headaches
- Reduced urination frequency
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to increase your water intake to prevent dehydration and its associated risks, including UTIs.
Conclusion
The link between dehydration and urinary tract infections is clear. When you’re dehydrated, your body’s ability to flush out bacteria diminishes, increasing the risk of infection. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day is one of the simplest and most effective ways to prevent UTIs and maintain a healthy urinary system. By prioritizing hydration, you’re not only helping prevent UTIs but also supporting your overall health and well-being.








One thought on “The Connection Between UTIs and Dehydration”
Comments are closed.