Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be painful and disruptive, especially when they occur repeatedly. Preventing recurrent UTIs requires a combination of lifestyle changes, hygiene practices, and sometimes medical intervention. This article provides practical steps to minimize the chances of developing recurrent UTIs and improve urinary tract health.

What Are Recurrent UTIs?
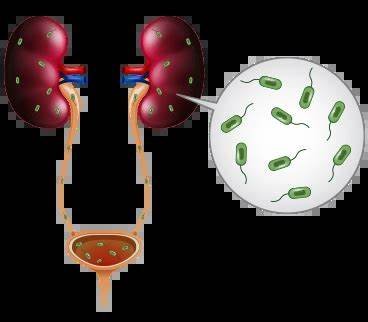
Recurrent UTIs are defined as having two or more infections in six months or three or more infections in a year. They often occur due to incomplete treatment of the initial infection, anatomical issues, or behaviors that increase the risk of bacterial growth. Women are more prone to recurrent UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
Tips for Preventing Recurrent UTIs
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract. Aim for at least 6–8 glasses of water daily. Staying hydrated dilutes urine, making it harder for bacteria to grow.
Practice Good Hygiene
Proper hygiene is essential in preventing UTIs. For women, always wipe from front to back after using the bathroom to avoid transferring bacteria from the anus to the urethra. Teach children and elderly family members proper hygiene to reduce their risk as well.
Empty Your Bladder Regularly
Holding urine for long periods can allow bacteria to multiply in the bladder. Empty your bladder every 2–4 hours and always urinate after sexual activity to flush out bacteria introduced during intercourse.
Avoid Irritating Products
Harsh soaps, bubble baths, and feminine hygiene sprays can irritate the urethra and increase the risk of infections. Use mild, unscented products for personal care.
Wear Breathable Clothing
Tight or non-breathable clothing can trap moisture, creating a favorable environment for bacteria. Opt for cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothes to keep the genital area dry and comfortable.
Dietary Changes to Prevent Recurrent UTIs
Include Cranberries
Cranberries contain compounds that may prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls. Drinking cranberry juice or taking cranberry supplements can be beneficial, though they are not a substitute for medical treatment.
Increase Vitamin C Intake
Vitamin C helps acidify urine, which may make it less hospitable to bacteria. Add citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers to your diet for a natural boost.
Eat Probiotic-Rich Foods
Probiotics, such as those found in yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods, help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the body, which can reduce UTI risk.
Medical Interventions for Preventing Recurrent UTIs
Antibiotic Prophylaxis
For individuals prone to recurrent UTIs, doctors may prescribe low-dose antibiotics to be taken daily, after sexual activity, or at the first sign of symptoms. This strategy helps reduce the frequency of infections.
Vaginal Estrogen Therapy
Postmenopausal women are more susceptible to recurrent UTIs due to decreased estrogen levels, which can thin the vaginal walls and reduce natural defenses. Vaginal estrogen creams or suppositories may help restore balance and prevent infections.
Address Underlying Conditions
Certain medical conditions, like kidney stones, diabetes, or bladder dysfunction, can contribute to recurrent UTIs. Treating these underlying issues is critical for long-term prevention.
Preventing UTIs in Specific Groups
Women
- Use unscented menstrual products to avoid irritation.
- Avoid diaphragms and spermicides, which can increase UTI risk. Opt for other contraceptive methods.
Children
- Ensure they drink enough water and use the bathroom regularly.
- Teach proper wiping techniques.
Elderly
- Monitor hydration and address incontinence issues.
- Ensure good hygiene in individuals requiring assistance with daily care.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience recurrent UTIs despite following preventive measures, consult a healthcare provider. They may recommend:
- Advanced imaging tests to identify anatomical abnormalities.
- Urine cultures to determine the exact bacteria causing infections.
- Urological evaluations for conditions like bladder dysfunction or urinary reflux.
Conclusion
Recurrent UTIs can be frustrating, but with the right strategies, they are preventable. Focus on staying hydrated, maintaining proper hygiene, and making dietary changes to support urinary health. Seek medical advice for persistent cases to explore tailored solutions. By taking proactive steps, you can reduce the frequency of UTIs and lead a healthier, more comfortable life.