Proper hydration is essential for maintaining overall health, and it plays a significant role in bladder health. The bladder is a vital organ in the urinary system that stores urine, and it requires adequate water intake to function optimally. Staying hydrated not only supports kidney function but also helps prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, and other bladder-related issues. This article will explore how hydration impacts bladder health and offer tips for maintaining proper fluid intake.

How Hydration Affects the Bladder
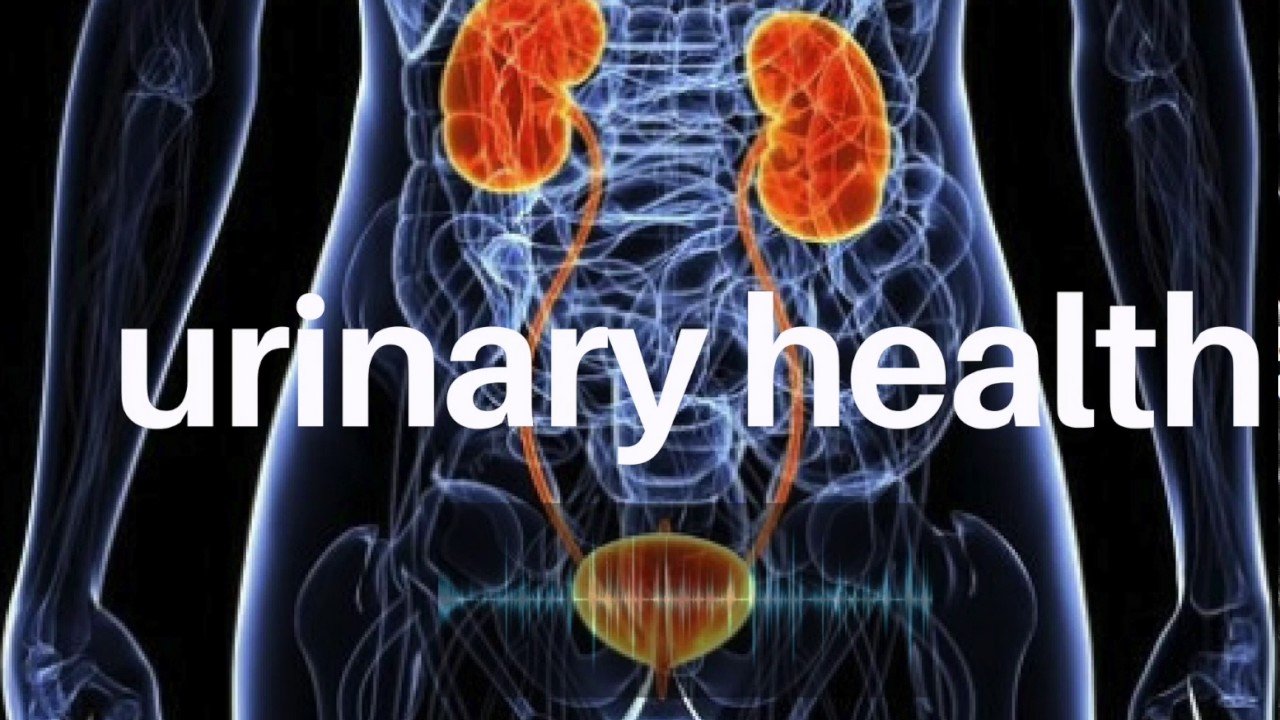
The bladder, as a storage organ for urine, relies on the kidneys to filter waste products and excess fluids from the body. Drinking enough water helps to flush out toxins and maintain the volume and consistency of urine, which can reduce the risk of urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and other complications. Hydration ensures that the kidneys work efficiently, processing waste properly and preventing harmful substances from accumulating in the bladder.
- Prevents Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
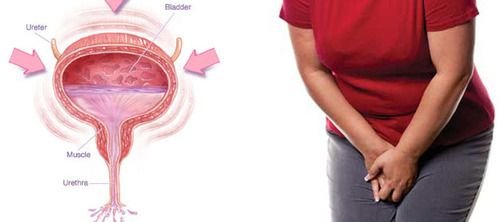
Hydration helps to dilute the urine and flush out bacteria that may otherwise accumulate in the bladder. When the urine is concentrated, bacteria can thrive and cause infections. Drinking enough water encourages frequent urination, which reduces the likelihood of bacteria taking hold in the urinary tract. - Reduces the Risk of Kidney Stones
Proper hydration helps prevent the formation of kidney stones by keeping the urine diluted. When you’re not drinking enough water, the urine becomes concentrated, and waste products can crystallize, forming stones. Drinking plenty of water helps ensure these substances are flushed out before they have a chance to build up. - Maintains Healthy Urinary Flow
Drinking water helps keep the urinary system flowing smoothly by promoting frequent urination. Regular urination reduces the chances of urinary retention, which can lead to infections and bladder overactivity. It also reduces the pressure on the bladder walls, promoting healthy bladder function.
How Much Water Should You Drink?
The amount of water an individual needs can vary based on factors like age, activity level, climate, and overall health. However, a general guideline is to drink about 8 glasses (64 ounces) of water a day. Some people may need more, especially if they are physically active or live in a hot climate. On the other hand, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as kidney problems, may need to adjust their fluid intake accordingly. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the right amount of water for your individual needs.
Signs of Dehydration and Their Impact on the Bladder
When the body is dehydrated, the urine becomes more concentrated, which can lead to a range of bladder issues. Some signs of dehydration include:
- Dark-colored urine: Dark yellow or amber-colored urine is a sign that you may not be drinking enough fluids.
- Urinary discomfort: Dehydration can cause the bladder to become irritated, leading to pain or a burning sensation during urination.
- Infrequent urination: If you’re not urinating regularly, it could be a sign that you’re not drinking enough water.
- Increased risk of infections: Dehydration weakens the body’s natural ability to flush out bacteria, making it more susceptible to UTIs and bladder infections.
It’s crucial to listen to your body’s signals and adjust your water intake to prevent dehydration and its associated bladder issues.
Hydration Tips for Maintaining Bladder Health
To maintain proper hydration and promote bladder health, consider the following tips:
- Drink Water Regularly Throughout the Day
Rather than consuming large amounts of water all at once, try to sip water consistently throughout the day. This helps maintain hydration levels without overwhelming the kidneys. - Monitor Urine Color
Check the color of your urine to ensure you’re adequately hydrated. Clear or light yellow urine is a good sign of proper hydration, while dark urine indicates that you may need to drink more water. - Incorporate Water-Rich Foods
Fruits and vegetables, such as cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges, are rich in water content and can help you stay hydrated. Including these foods in your diet is a great way to support hydration.
The Bottom Line
Hydration plays a key role in supporting bladder health and preventing various urinary issues. Drinking enough water helps flush out toxins, prevent infections, and reduce the risk of kidney stones and other bladder-related complications. To maintain proper hydration, aim to drink at least 8 cups of water a day, adjust your intake based on activity levels, and listen to your body’s signals to prevent dehydration. By prioritizing hydration, you can promote overall health and support the proper function of your urinary system.