Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common health issues that can affect anyone, though women are more prone to them. Recognizing the symptoms early and knowing when to seek medical help can prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.

Common Symptoms of a UTI
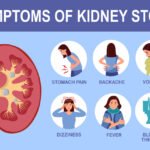
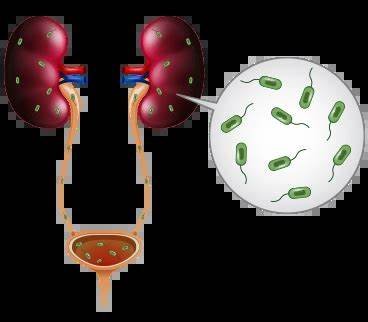
UTIs can affect different parts of the urinary system, including the urethra, bladder, and kidneys. The symptoms may vary depending on the location and severity of the infection.
1. Frequent Urination
A common sign of a UTI is the frequent urge to urinate, even if little urine comes out. This urgency often disrupts daily activities and sleep.
2. Burning Sensation During Urination
A painful, burning feeling while urinating is a hallmark symptom of a UTI. It occurs due to inflammation in the urinary tract caused by bacteria.
3. Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine
Urine that appears cloudy or has a strong, unpleasant odor may indicate the presence of bacteria or pus in the urinary tract.
4. Blood in the Urine (Hematuria)
Pink, red, or cola-colored urine may signal blood in the urinary system. While this can be alarming, it’s often a sign of a UTI that needs medical attention.
5. Lower Abdominal Pain or Pressure
Discomfort or pressure in the lower abdomen or pelvic area is common with bladder infections, a type of UTI.
6. Fatigue or General Malaise
UTIs can make you feel tired or unwell, especially if the infection spreads beyond the bladder.
7. Pain in the Flank or Back
Pain in the back or sides of the body may indicate that the infection has reached the kidneys, which is more severe and requires immediate attention.
8. Fever, Chills, and Nausea
Kidney infections can cause systemic symptoms like fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. These symptoms suggest a serious infection that may require hospitalization.
When to See a Doctor
While some mild UTIs may resolve on their own, many require medical treatment to avoid complications. You should see a doctor in the following situations:
1. Persistent Symptoms
If your symptoms last more than two days or worsen despite self-care measures, consult a doctor.
2. Blood in Urine
Hematuria is a sign of a more severe infection or other underlying conditions that need evaluation.
3. Fever and Back Pain
Fever, chills, and back or flank pain could mean the infection has spread to your kidneys. Seek immediate medical attention.
4. Recurring UTIs
If you experience frequent UTIs, a doctor can identify underlying causes and suggest preventive measures.
5. UTI During Pregnancy
Pregnant women with UTI symptoms should seek medical care promptly, as untreated infections can affect the baby’s health.
6. Underlying Health Conditions
If you have diabetes, a weakened immune system, or kidney problems, don’t delay seeing a doctor for UTI symptoms.
7. Children or Elderly
UTI symptoms in children and older adults can differ from those in younger adults. If they exhibit unusual behavior, fever, or discomfort, seek medical advice.
How UTIs Are Diagnosed
A doctor will usually diagnose a UTI based on your symptoms and a urinalysis, which detects bacteria, white blood cells, or blood in the urine. In more complicated cases, imaging tests or a urine culture may be needed to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Treatment Options for UTIs
1. Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the most common treatment for UTIs. Your doctor will prescribe a specific antibiotic based on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria.
2. Pain Relief
Over-the-counter medications or prescribed pain relievers can help ease discomfort during urination.
3. Increased Hydration
Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria out of your urinary tract and supports faster recovery.
4. Hospitalization for Severe Cases
For kidney infections or UTIs that don’t respond to oral antibiotics, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics may be necessary.
Preventing UTIs
While recognizing symptoms is essential, prevention is the best strategy. To reduce your risk of UTIs:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Practice good personal hygiene, such as wiping front to back.
- Urinate after sexual activity to flush out bacteria.
- Avoid holding in urine for extended periods.
- Wear breathable cotton underwear.
Conclusion
UTIs are uncomfortable but manageable infections if treated early. Symptoms like frequent urination, burning sensations, or cloudy urine should not be ignored. Knowing when to see a doctor is crucial, especially if the infection spreads or symptoms worsen. By staying proactive about prevention and seeking medical care when necessary, you can maintain good urinary health and avoid complications.